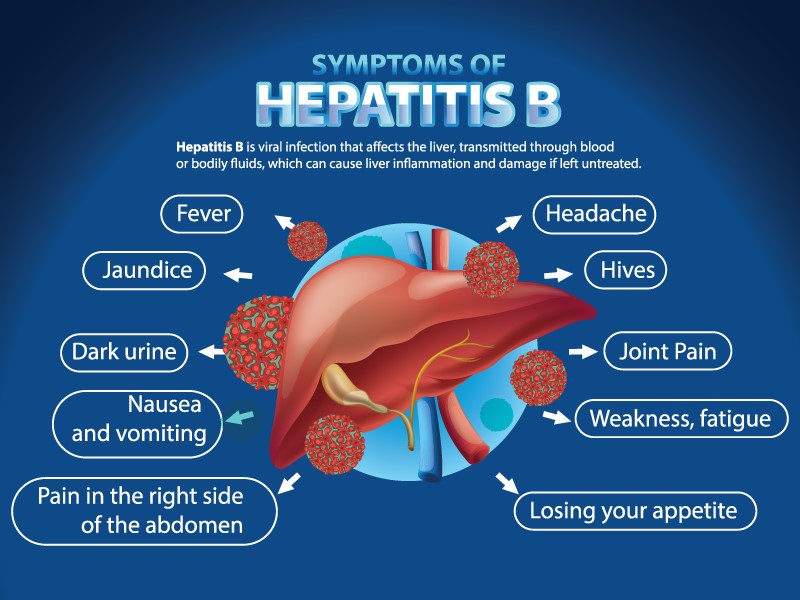
Hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver. Initial and acute effects of hepatitis include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, dark urine, pale stools, jaundice and joint pain. Chronic and severe effects of hepatitis include cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer.
Types of Hepatitis
Non-Viral Hepatitis: This is not caused by a viral infection but by other factors like alcohol, toxins, autoimmune diseases, certain medications, etc.
Viral Hepatitis: This is caused by a viral infection. There are five types of viral hepatitis namely: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D and Hepatitis E.
Hepatitis A: This is caused by the Hepatitis A Virus (HAV). It’s a very contagious disease. It transmitted through consumption of food or water contaminated with the virus, close person-to-person contact or poor hygiene. It usually causes mild symptoms and goes away without treatment.
Hepatitis C: This is caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). It is transmitted through contact with infected blood. You might not have symptoms, but screening tests can detect the infection. New medications can cure it. But without treatment, it can cause chronic liver disease and lead to cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer.
Hepatitis D: This is caused by the Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV). HDV requires the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) to replicate and cause infection. The main cause of Hepatitis D is coinfection with both viruses, transmitted through contact with infected blood or body fluids, such as via injection or sex. You cannot get Hepatitis D without already having Hepatitis B.
Hepatitis E: This is caused by the Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). It is transmitted through transmitted through contaminated drinking water and food. Other less common routes include eating undercooked meat from infected animals like pigs or deer, blood transfusions, and vertical transmission from a pregnant woman to her foetus.
Hepatitis B: This is caused by the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). The common transmission routes of hepatitis B are similar to those of HIV i.e. unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles or syringes, infected mother to her child during birth. It can also be spread through sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes, or from unsterilized medical equipment. Like HIV, Hepatitis B has no cure.
Acute hepatitis B can often go away on its own, particularly in healthy adults who are able to clear the virus from their bodies naturally. However, if the virus persists for more than six months, the infection becomes chronic, and it is an incurable condition that requires lifelong management to prevent serious complications like cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
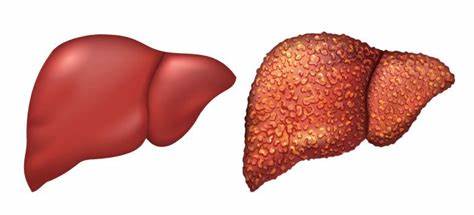
Patients with chronic hepatitis B often need to take medication for life. The drugs do not eliminate the virus from the body but prevent it from multiplying, which lowers the chances of developing serious liver conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer. When treatment is started is decided by a doctor based on factors like the level of viral activity, liver inflammation, and your overall health.
Patients with chronic hepatitis B need regular medical check-ups to monitor their liver health whether you’re taking medication or not.
The liver functions as the body’s main filter and metabolic center, performing roles like detoxifying blood, processing nutrients from food, and producing bile for digestion. It also regulates blood clotting, converts ammonia to urea, stores energy as glycogen, and helps manage cholesterol and hormone levels. If the liver gets damaged and cannot function again, the patient will need liver transplant to live a normal life.
Many people are unaware of their chronic hepatitis B status and they inadvertently spread the virus to other people. For some people, they know. They are aware. Some even take their medications. Yet, they choose not to disclose their status to their partners, putting the lives of their partners at risk.
Many married men have infected their innocent wives with the virus through extramarital affairs. Similarly, many married women have infected their innocent husbands with the virus.
Before you have sex with your partner, make sure you know his or her hepatitis B status. The rate at which people are contracting the virus is alarming. Stay safe!
Photo Credits:www.pathkindlabs.com, www.consumerhealthdigest.com
Related:
HIV/AIDS FROM A CHEATING PARTNER





























One thought on “HEPATITIS B EPIDEMIC”